What is Color Tempreture
Color temperature is a characteristic of visible light that has important applications in lighting and other fields. Color temperature is conventionally stated in the unit of absolute temperature, the kelvin, having the unit symbol K.
Absolute temperature (K) was presented in 1848 by the British physicist Keivin. He considers starting point temperature is 273.16 ℃ below zero centigrade. Absolute temperature calculation, therefore, is 273.15 ℃, combined with the Celsius temperature usually used, such as body temperature is 36 ℃, and absolute temperature 309 k.
The color temperature of a light source is the temperature of an ideal black body radiator that radiates light of comparable hue to that of the light source. Is a standard blackbody, heating temperature to a certain extent the color started from deep red to pale red – orange – white – blue and white – blue change gradually. Using this light color changing characteristic, the light from light source color hue to the light of the blackbody at the same time, we will absolute temperature blackbody was known as the color temperature of the light source. It does not make sense to speak of the color temperature of e.g. a red or a green.

Color Tempreture
Color temperature affects the atmosphere of the space. Color temperatures over 5,000K are called cool colors (blueish white), while lower color temperatures (2,700-3,000 K) are called warm colors (yellowish white through red). Under 3300K color temperature, light color has partial red phenomenon, is a kind of warm feeling to the person, above 5000k color temperature, color slants white, give a person a kind of cool feeling.
In addition, the different color temperature of light environment and medium temperature also affects the people of the surrounding environment’s color feeling. Take red light for example, under the red light source, people often cannot see the red color perfectly.
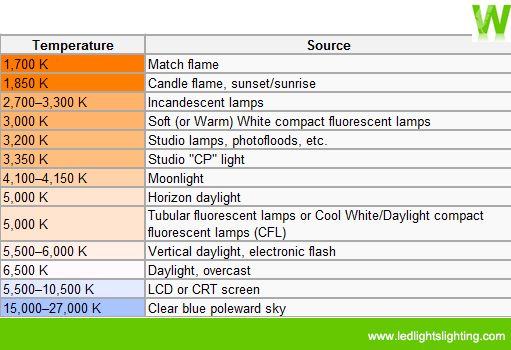
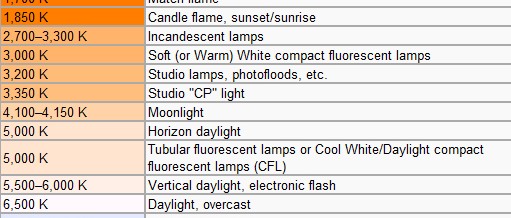
Color Tempreture Compare
ShareJUN
2016